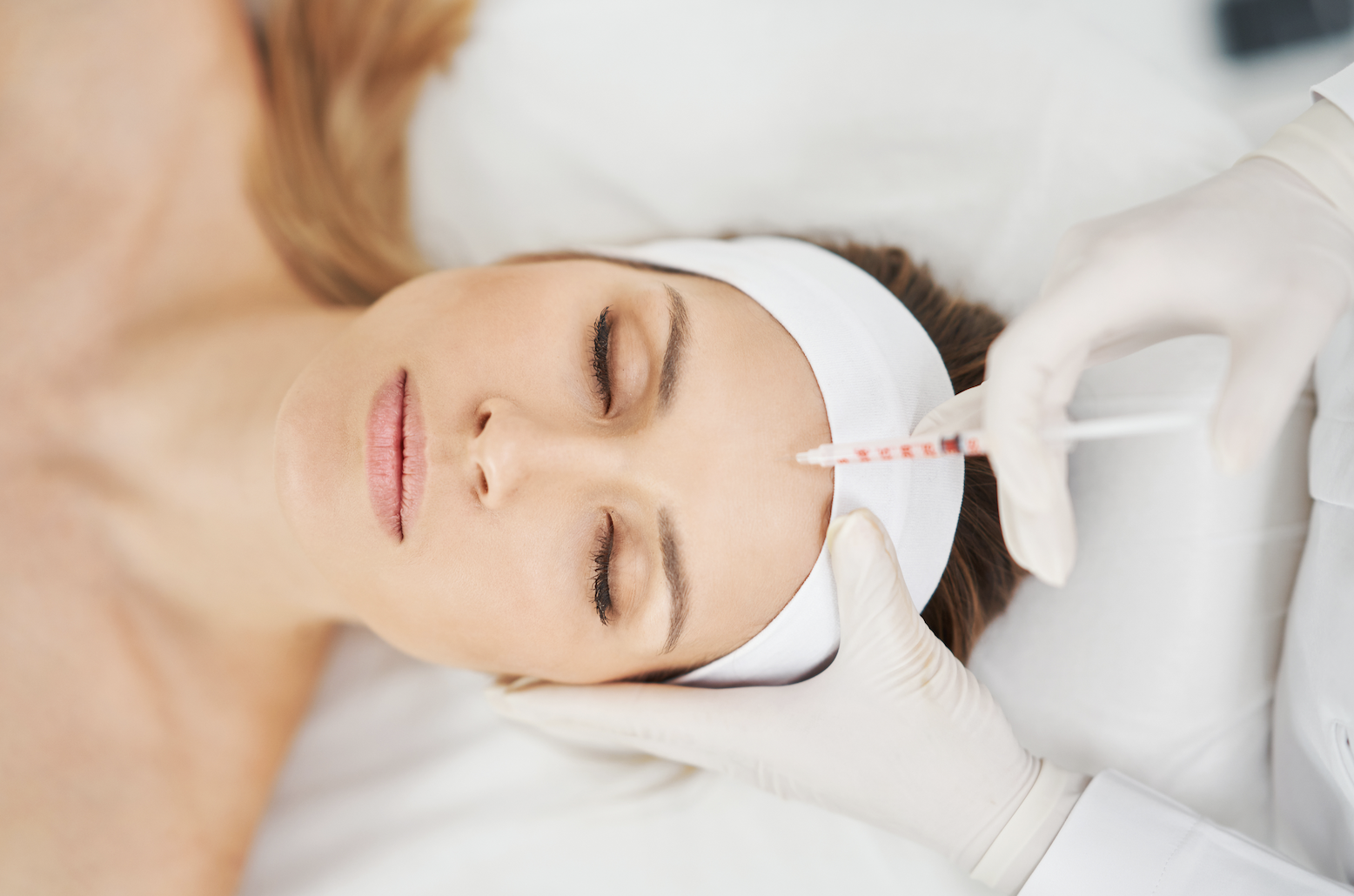
Botox, short for botulinum toxin, is a popular cosmetic treatment used to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles and fine lines. By injecting small amounts of Botox into specific muscles, it temporarily relaxes those muscles, smoothing out wrinkles and preventing them from deepening over time. One of the key advantages of Botox for aesthetic purposes is its ability to provide natural-looking results with minimal downtime. Unlike surgical procedures, Botox injections are quick, virtually painless, and require no recovery time, allowing patients to resume their daily activities immediately. Additionally, Botox is highly customizable, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatments to each individual’s unique facial anatomy and desired outcome. With its proven safety record and ability to deliver noticeable, yet subtle improvements to the appearance of wrinkles, Botox remains a popular choice for those seeking to achieve a more youthful and refreshed appearance without undergoing invasive surgery.
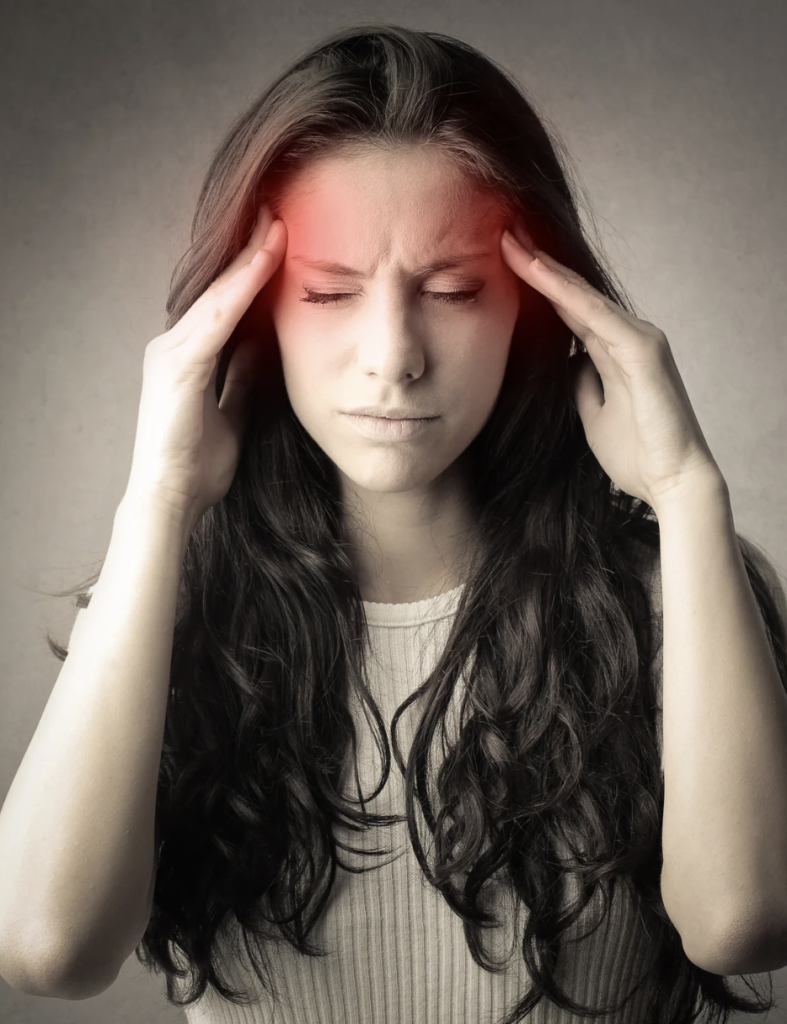




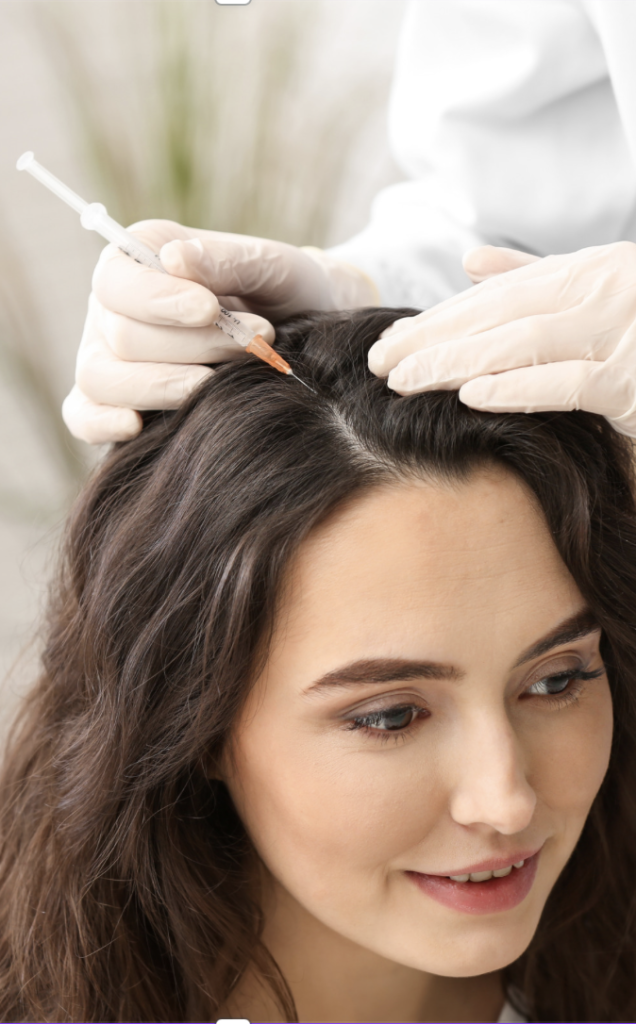
Botox, or botulinum toxin, is not only used for cosmetic purposes but also as a preventive treatment for chronic migraines. When injected into specific muscles of the head and neck, Botox blocks the release of certain neurotransmitters involved in pain signaling, thereby reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks. One of the key advantages of Botox for migraine treatment is its long-lasting effects, with results typically lasting for several months. Unlike oral medications, which may cause systemic side effects, Botox injections target the affected area directly, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. Additionally, Botox for migraines is a non-invasive procedure that can be performed in a healthcare provider’s office, requiring little to no downtime for patients. With its ability to provide significant relief for chronic migraine sufferers and improve their quality of life, Botox has become an important therapeutic option in the management of this debilitating condition.